

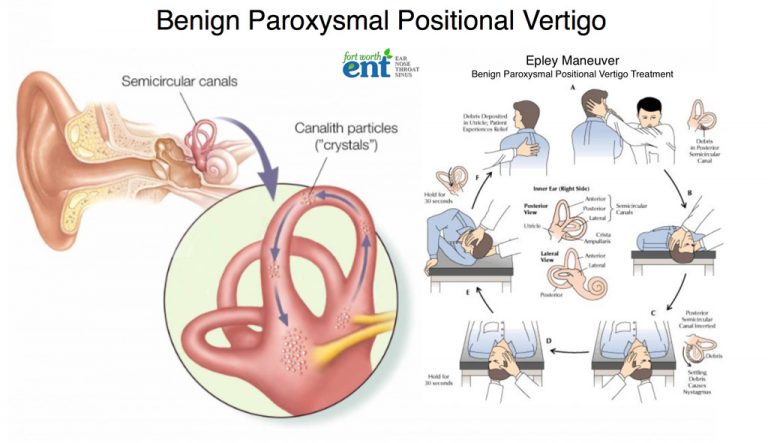
Last of all patient returns to sitting with his head maintained in that position.Turn the patient's head towards the ground i.e 45-60 degrees, hold this position for 2 minutes.Patient is taken from sitting to side-lying on the affected or unaffected side.Treatment for horizontal/lateral canal BPPV. Without any head movement, the patient is asked to move to the side-lying on the opposite side of the body, face towards the bed.Then the patient rapidly moves into side-lying to the affected side, face towards the ceiling.Physiotherapist places one hand under the bottom of the shoulder while the other hand supports the neck.Patient is asked to sit in a short sitting, head rotated to 45 degrees towards the unaffected ear.The patients should complete this maneuver, for which 1to 3 visits are required for resolution of symptoms. Bring the patient up into short-sitting.Hold this position for 20 seconds or until nystagmus and dizziness subside. Patient rotates 90 degrees from supine to side-lying.Hold position this position for 20 seconds, or until nystagmus and dizziness subside. Then rotate the head to 90 degrees to the opposite side.Hold this position for 30 seconds or until nystagmus and dizziness subside. The patient is rapidly reclined to a supine position with the neck slightly extended.The patient is in a long sitting position, head rotated 45 degrees to the affected side.Epley maneuver that employs gravity to move calcium build-up that causes benign positional paroxysmal vertigo.Physiotherapy involves repositioning procedure: Neurological testing uses to indicate vertigo of central origin. A magnetic resonance imaging scan may reveal a buildup of fluid or inflammation in the inner ear or a growth on the nerve. This scan uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create computerized, three-dimensional images of the ear and the nerve that carries signals from the inner ear to the brain. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Scans helps to obtain a closer look at the inner ear and its surrounding structures. These tests are utilized to measure the response of the inner ear to sound stimuli. The patient wears special goggles that record the eye movements while the patient is in the chair.Īudiologists analyzes eye movements and interpret how they relate to the health of the inner ear.Įlectrocochleography helps to determine if fluid buildup causes excess pressure in the inner ear, which can also lead to vertigo symptoms. The patient is seated in a mechanized chair that slowly rotates.

Followed by the audiologist analysis, the eye movement data is obtained by the goggles and also looks for patterns indicating an inner ear disorder as the cause of vertigo.Īudiologists use rotational chair testing to obtain information about whether vertigo is of peripheral or central origin. The infrared goggles worn by the patient records eye movements while caloric testing takes place. A variety of shapes, objects, and spots of light appear on the screen, and the patient is asked to perform certain tasks with eyes while keeping his head still. Videonystagmography testing takes place in a testing suite within an audiologist's office. Videonystagmography is done to evaluate the function of the inner ear using visual and sensory tests. Hearing tests also help to assess whether there is a problem with the nerve that connects the inner ear to the brain and whether dysfunction affects both ears. If the patient has trouble with this task or experiences rapid eye movements or blurred vision then the patient is referred for more tests. Eye movements are checked or the patient is asked to track an object from one point in space to another. Physical examination is done to look for signs and symptoms of vertigo. Family history and history of the condition affecting balance, hearing or any infection, injury, or surgery in the ear or brain.
The patient may be asked what the sensation of movement or dizziness is felt, how frequently it occurs, whether it occurs while moving in a particular way, certain times of the day, and whether hearing loss or ringing in the ears is also felt. To diagnose vertigo, medical history is taken from the patient, including details about the symptoms. Tests for vertigo are done to elicit nystagmus and to differentiate vertigo from other causes of dizziness such as hyperventilation syndrome, presyncope, disequilibrium, or psychiatric causes of lightheadedness.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
